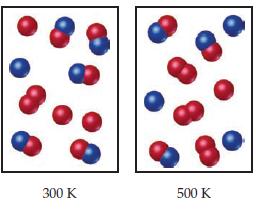
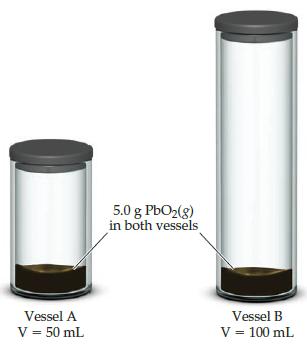
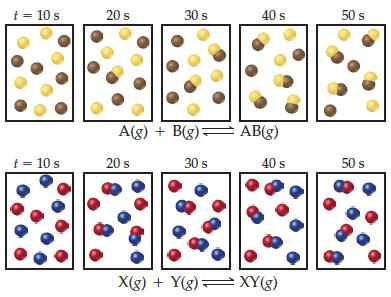
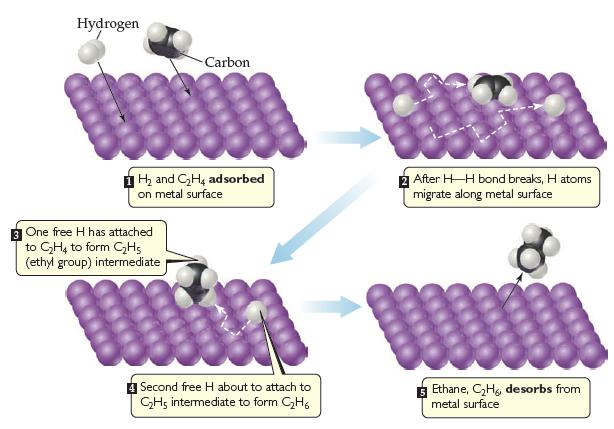
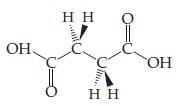
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()




![0.060 0.12 0.18 Concentration (M) 4 H]](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1603/1/0/0/4575f8d5f29cd7b01603100457972.jpg)




![(i) (ii) Time Time (iii) (iv) Time Time (v) (vi) Time Time 1/[A] [v]u] [v] In[A] 1/[A] [V]](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1602/7/6/3/8675f883c5b5d2ea1602763864858.jpg)
![(under conditions of constant [Cl2]) Time ION]/I](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1602/8/2/1/8525f891edc6da911602821851365.jpg)
![Experiment [X]o(M) [Z]o(M) Rate (M/s) 1 0.25 0.25 4.0 X 10' 0.50 0.50 3.2 x 102 3 0.50 0.75 7.2 x 10](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1602/8/2/2/1265f891feeec3011602822125920.jpg)