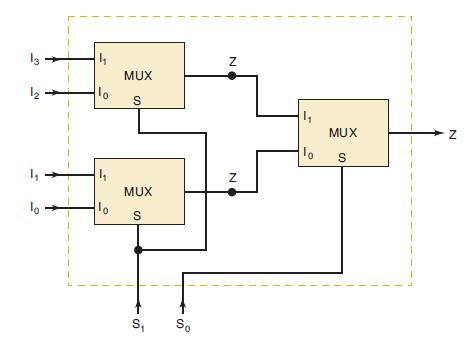
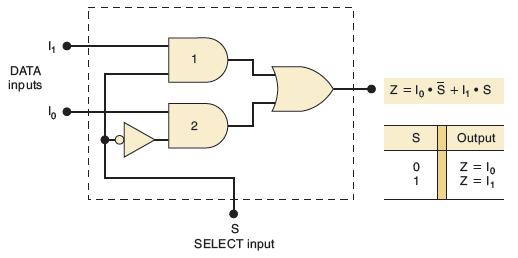
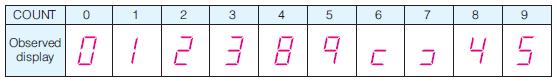
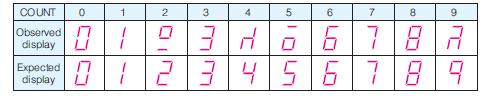
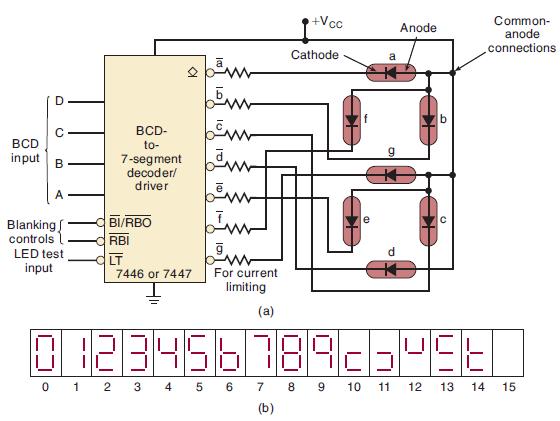
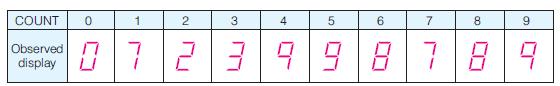
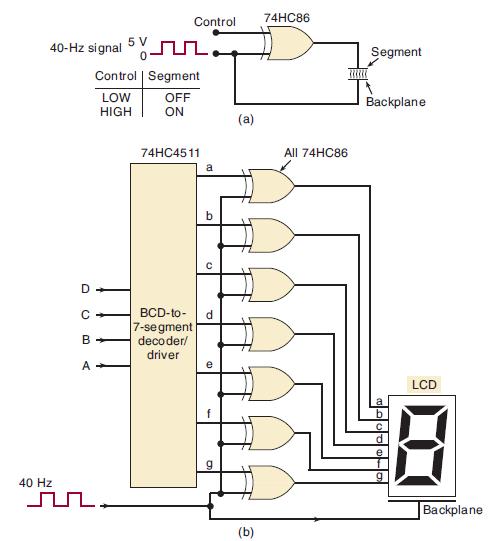
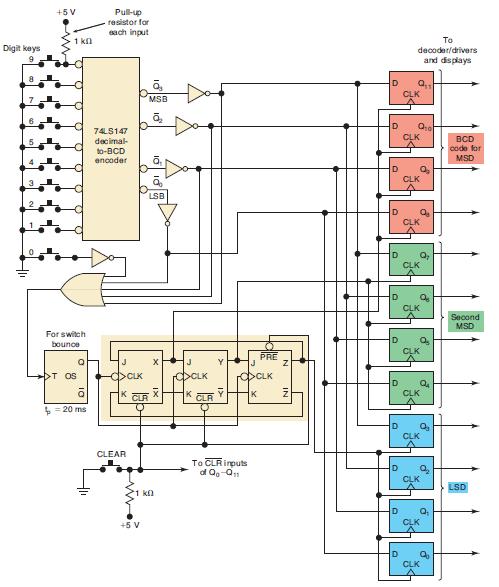
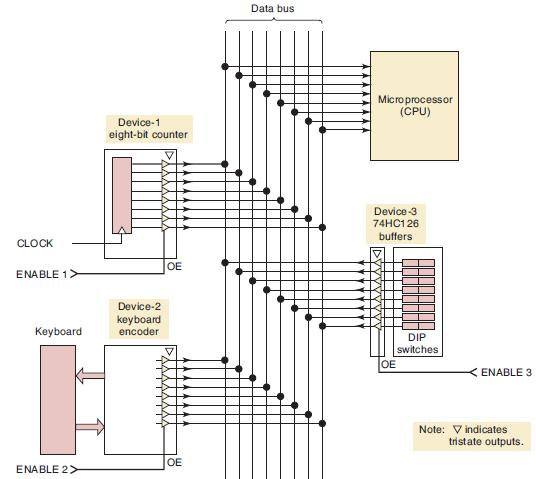
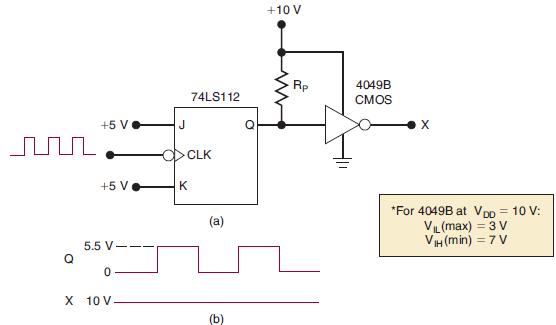
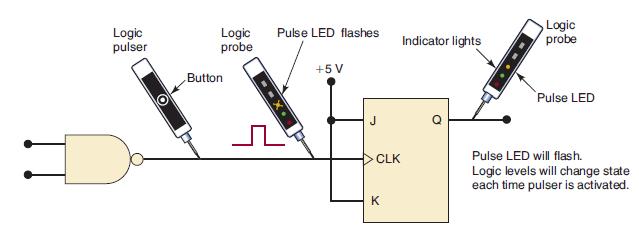
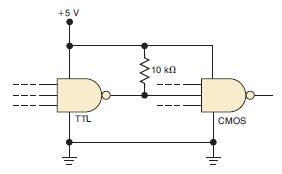
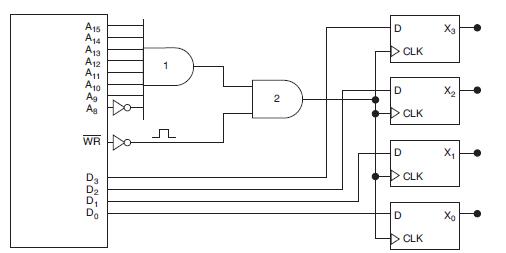
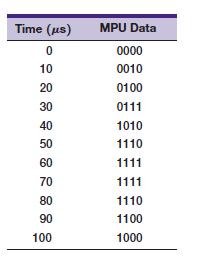
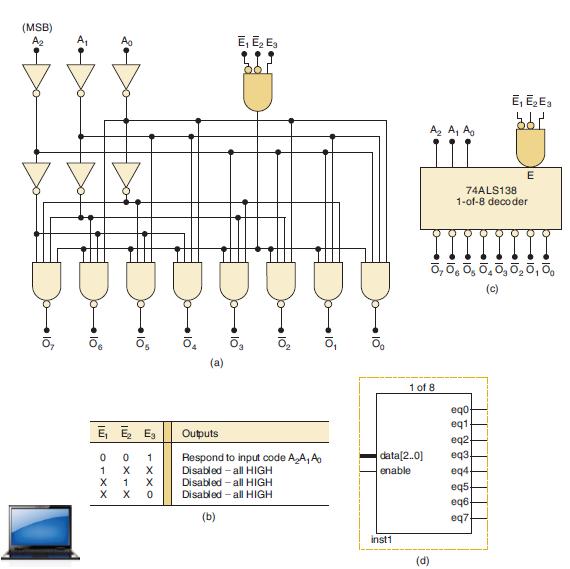
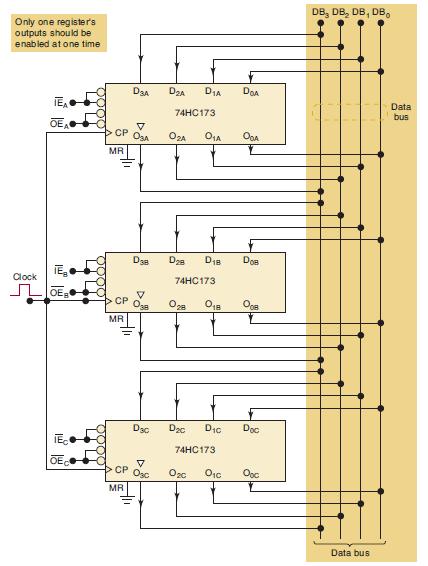
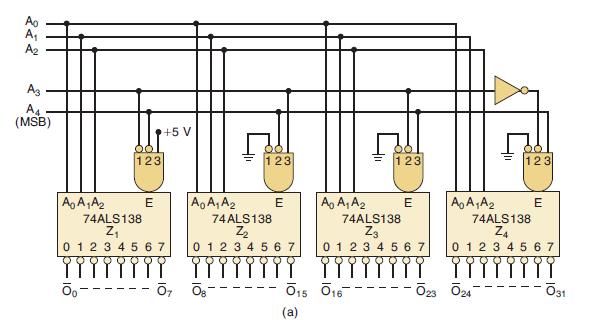
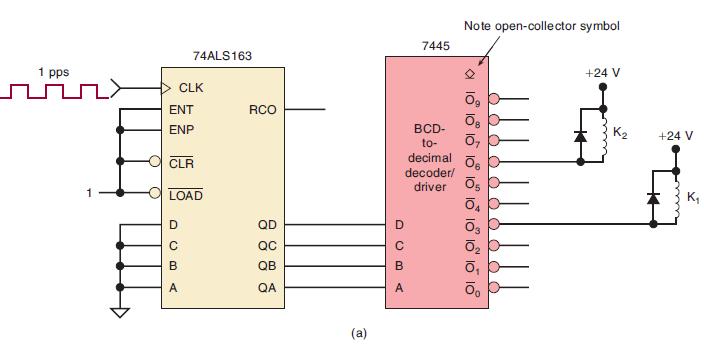
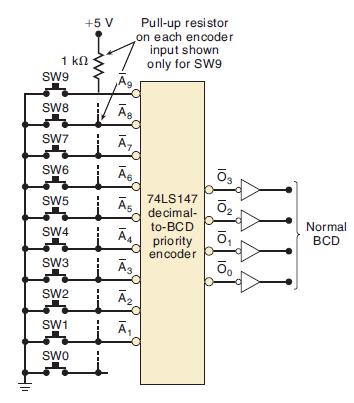
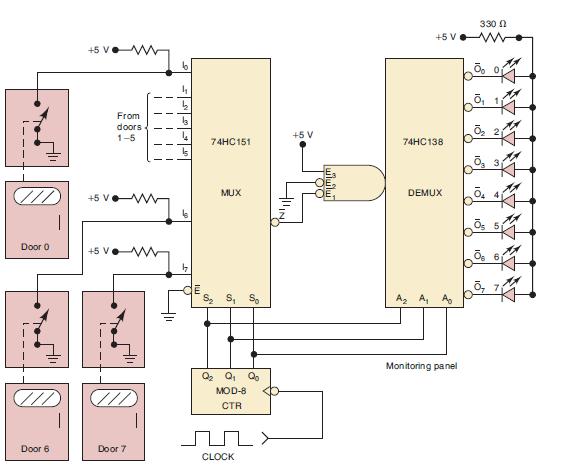
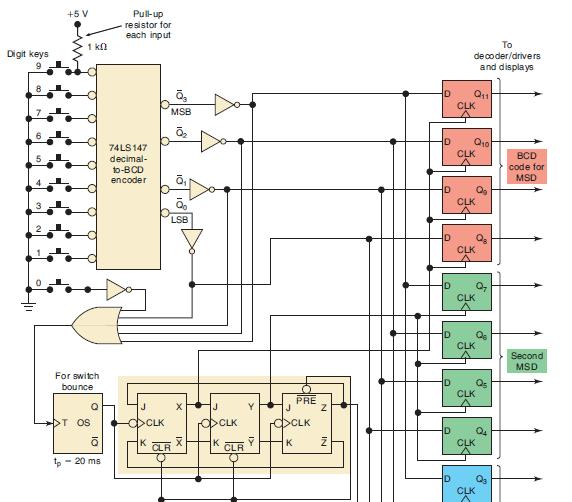
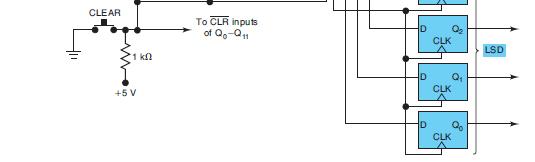
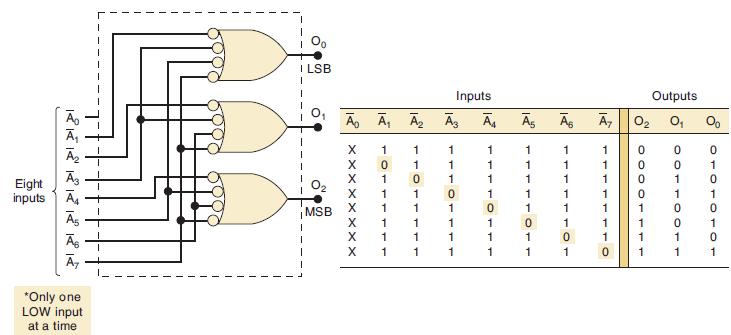
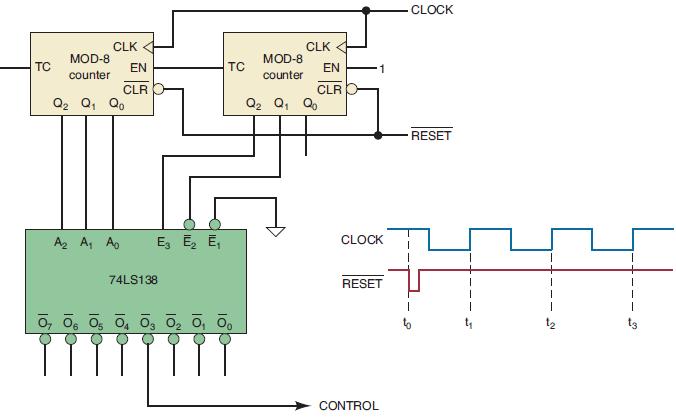
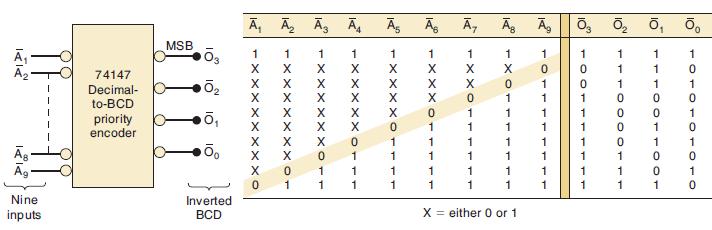
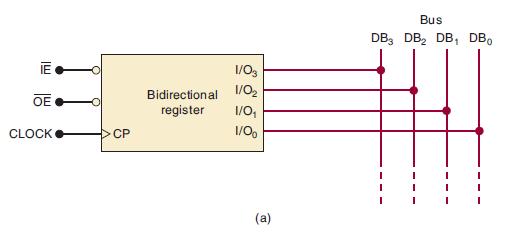
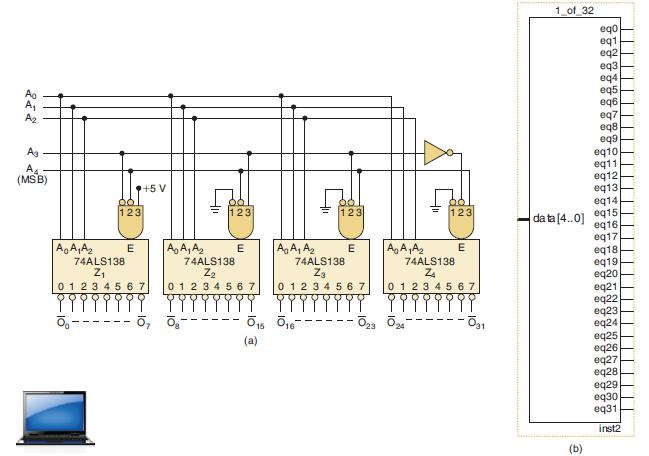
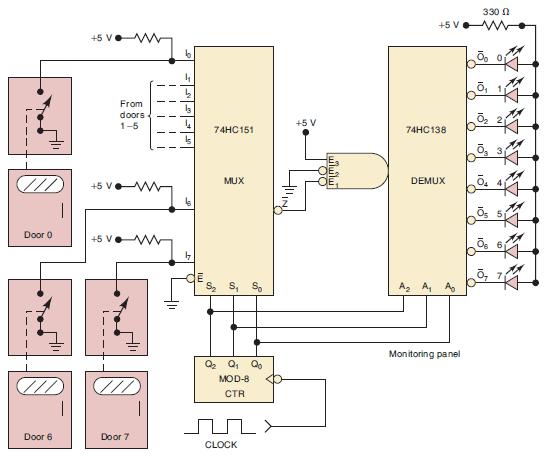
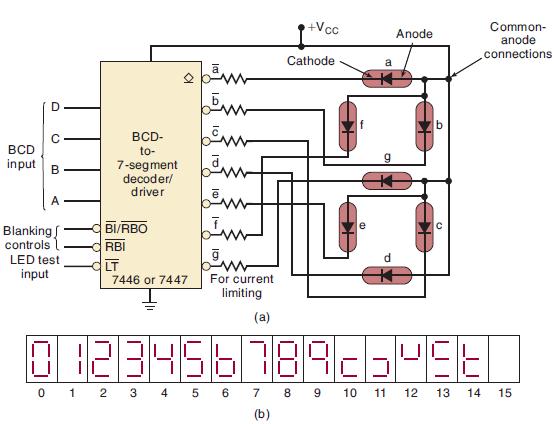
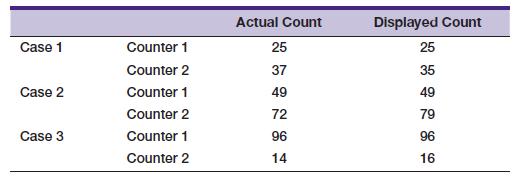
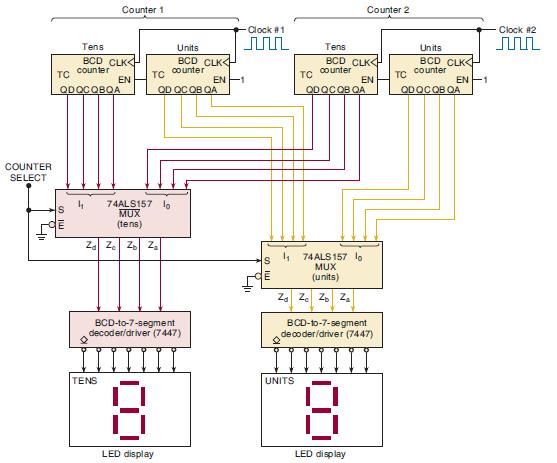
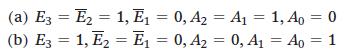![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


![(IN[n OUT[n] OUT[4] (IN[1] OUT[5] = (IN[2] = - - 3] + IN[n 2] + IN[n + IN[2] + IN[3] + IN[3] + IN[4] 1] +](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1700/2/0/3/77165570cfb7aedb1700203772653.jpg)
![Sample n IN[n] (V) OUT[n] (V) 1 0 0 2 0 0 3 0 0 4 0 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1700/2/0/3/61665570c60400201700203617527.jpg)