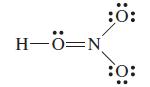
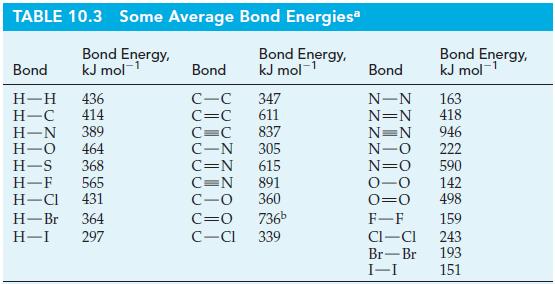
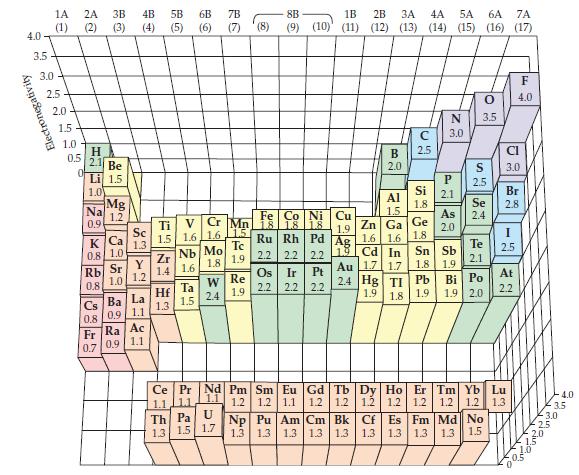
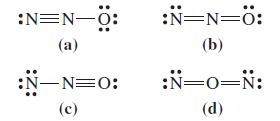![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


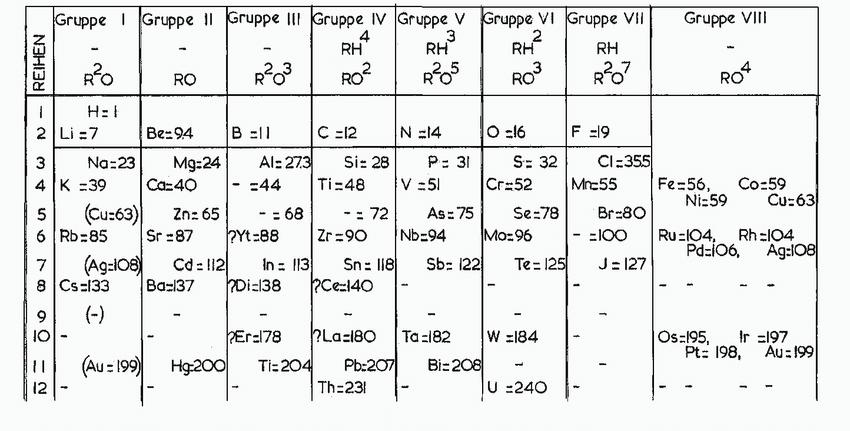
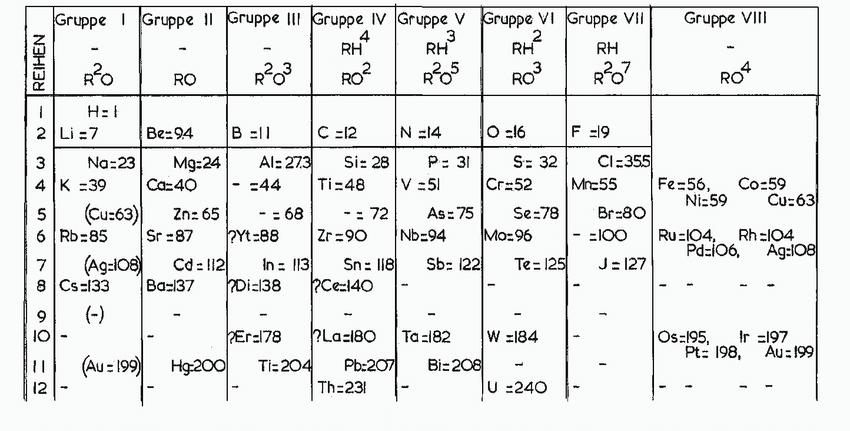
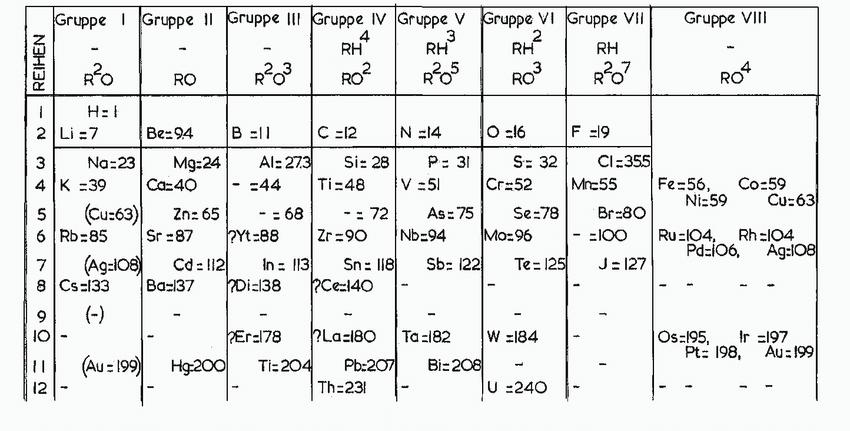
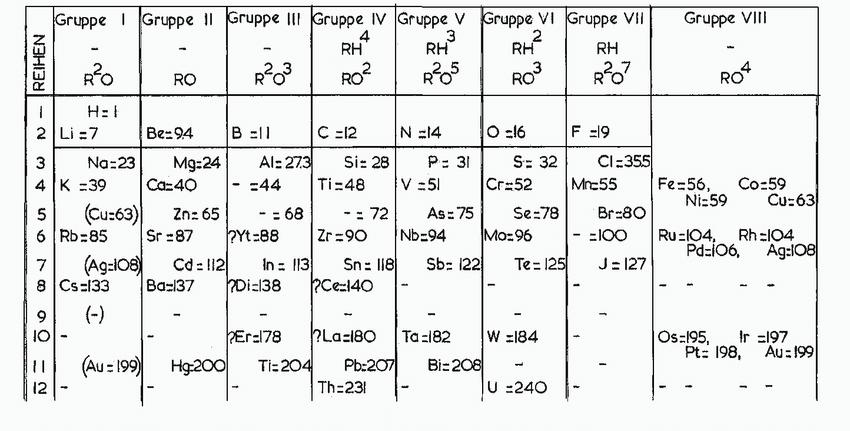
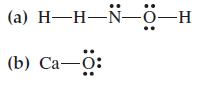
![(a) :0-C-0: (b) [.C=N:]](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1699/8/7/0/6326551f7a8cbb6a1699870631339.jpg)
![(a) cyanate ion (b) carbide ion (c) hypochlorite ion (d) nitrogen(II) oxide [:O-C=N:] [C=C:1- [:c-0:1 :N=0:](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1699/8/7/0/6856551f7dd68e101699870683832.jpg)
![(a) Mg:0: (b) [:O-N=0:1 (c) (d) [:S-C=N:] [:a::r [C: Cl :0](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1699/8/7/0/7156551f7fbb4ccb1699870714073.jpg)
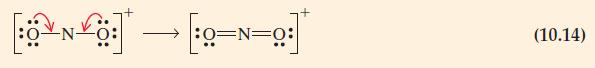

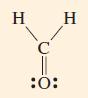
![(a) [H-C=C:] (b) :0: C :0: 72- O: (c) [CH3-CH-CH3]+](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1699/8/7/0/9346551f8d610e511699870931688.jpg)
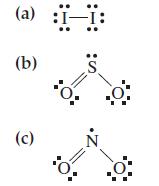
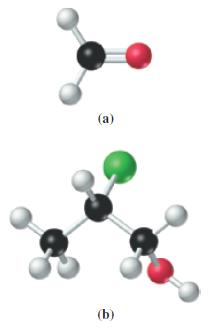
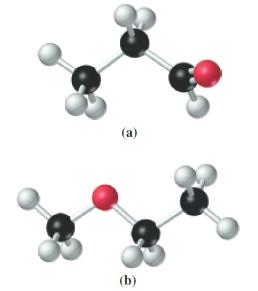
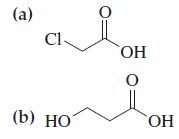
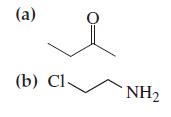
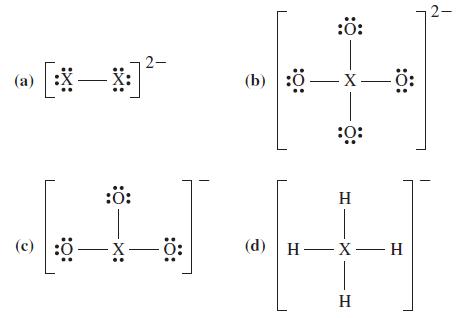
![G (c) 8-x=0 X :: :: :0: :0: H J 2- (d) [-x-:] :0: :0x- :0: :x- :0: -:](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1699/8/7/4/771655207d39c4f61699874770345.jpg)