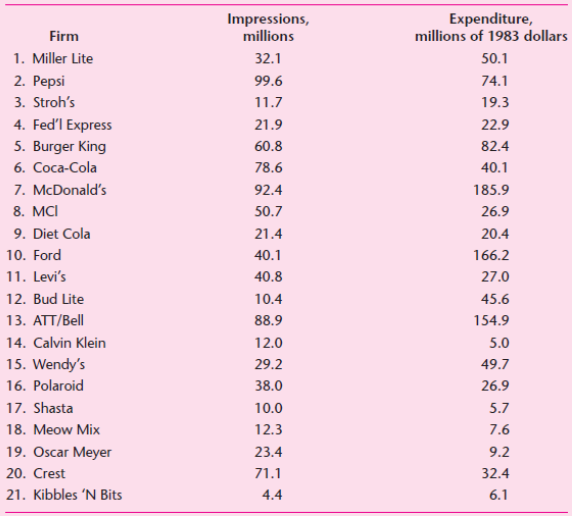
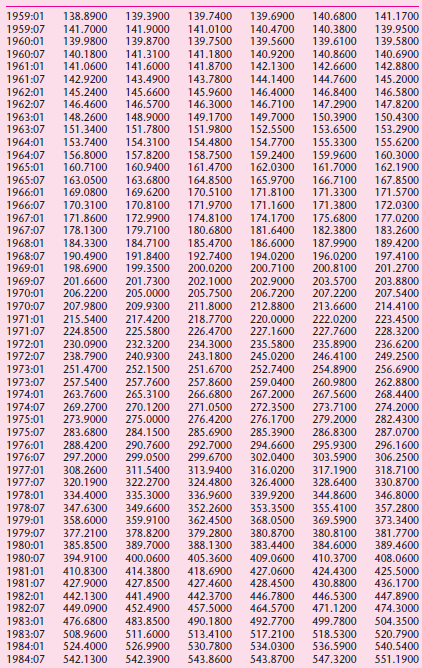
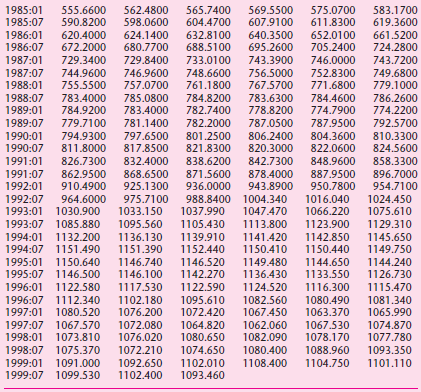
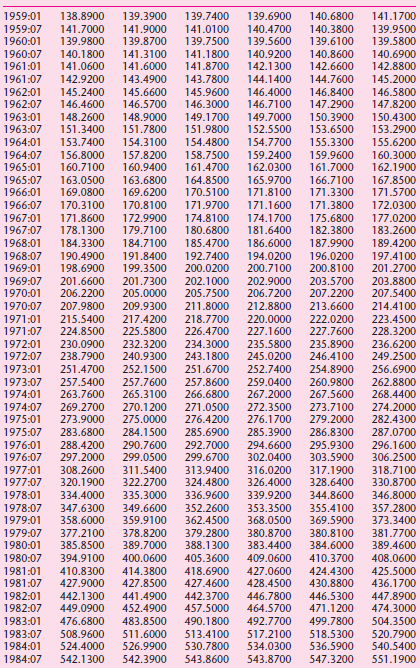
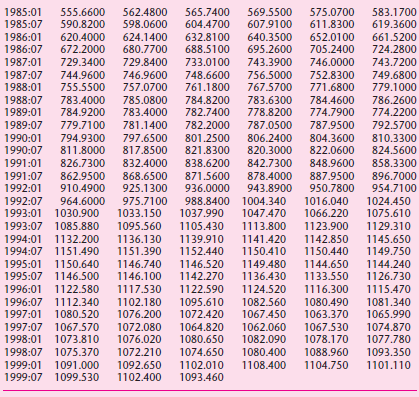
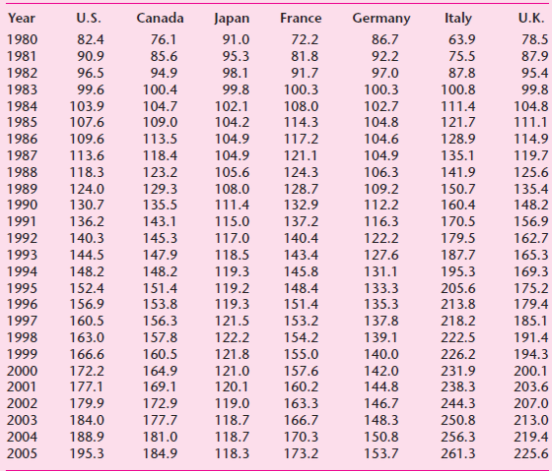
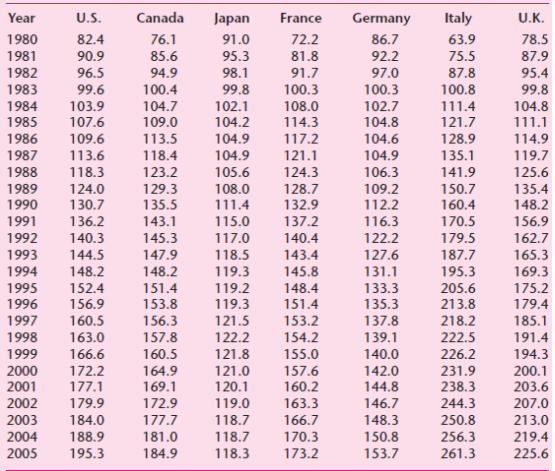
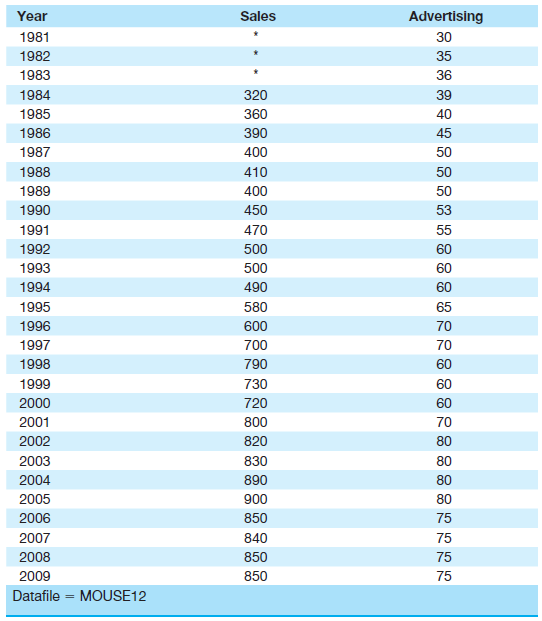
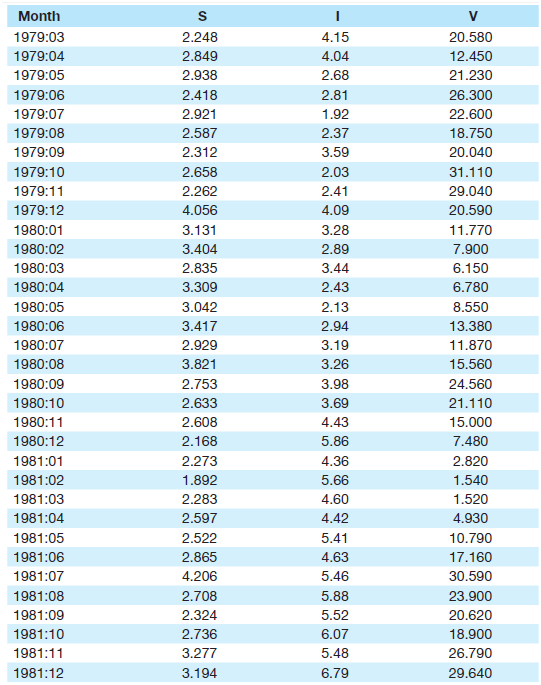
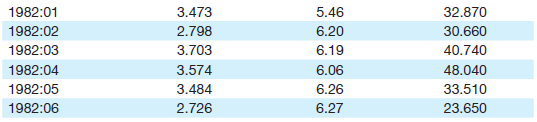
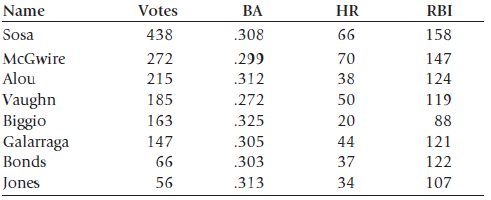
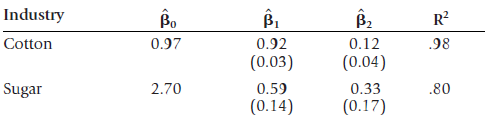
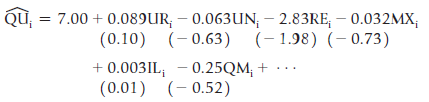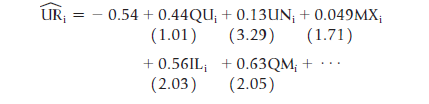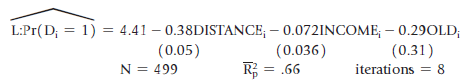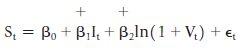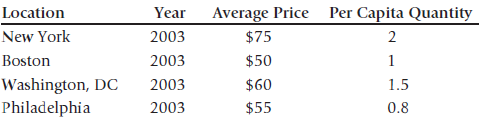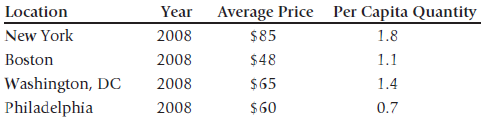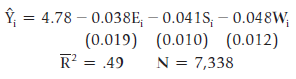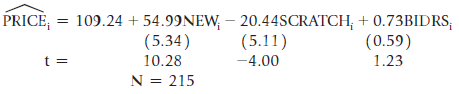![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


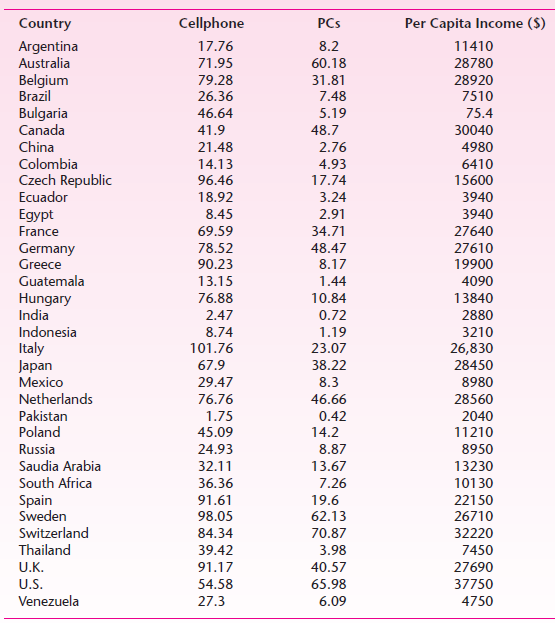
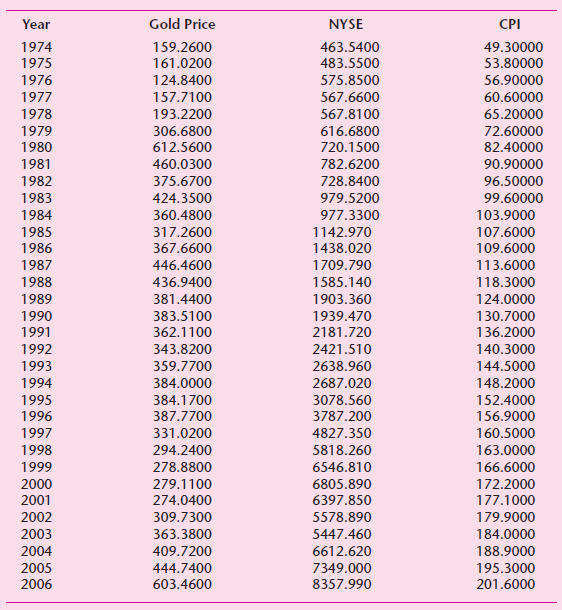
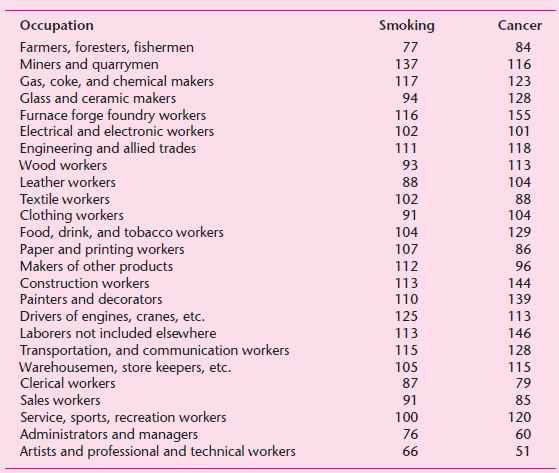
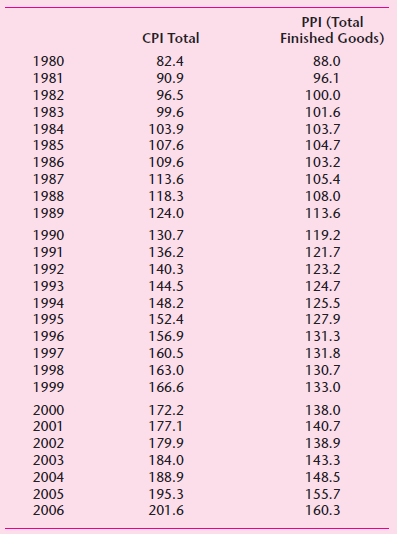
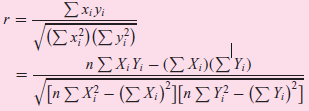
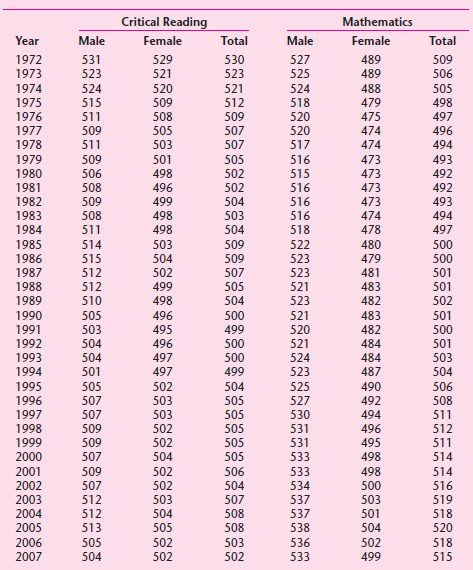
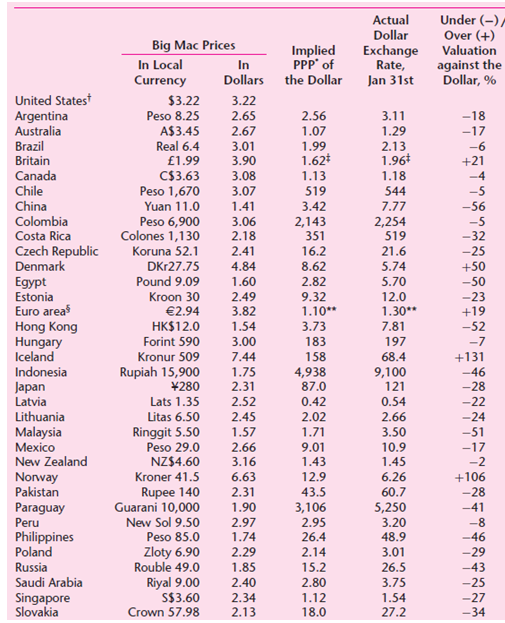
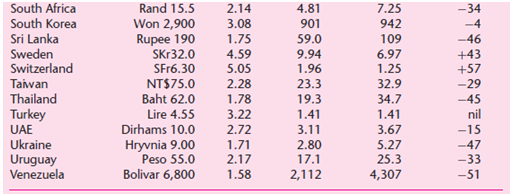
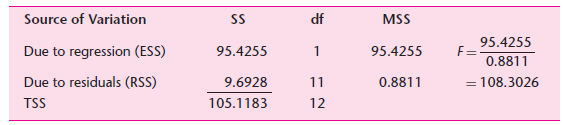

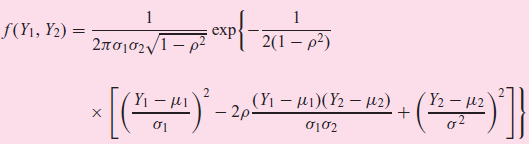
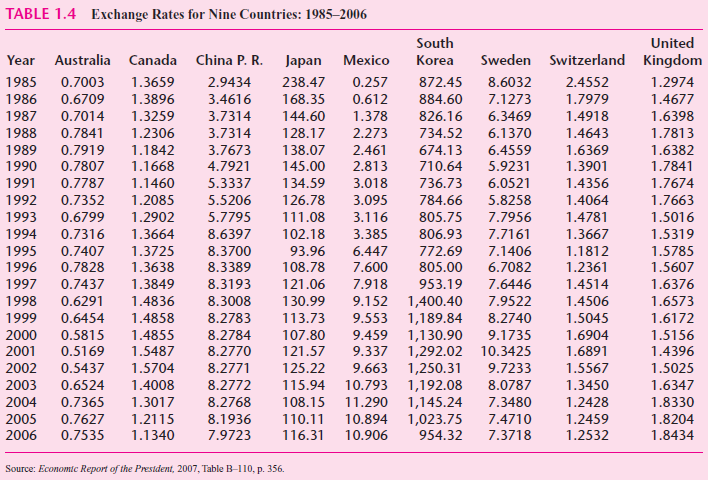
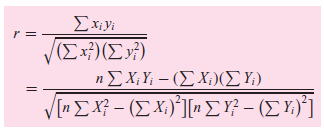
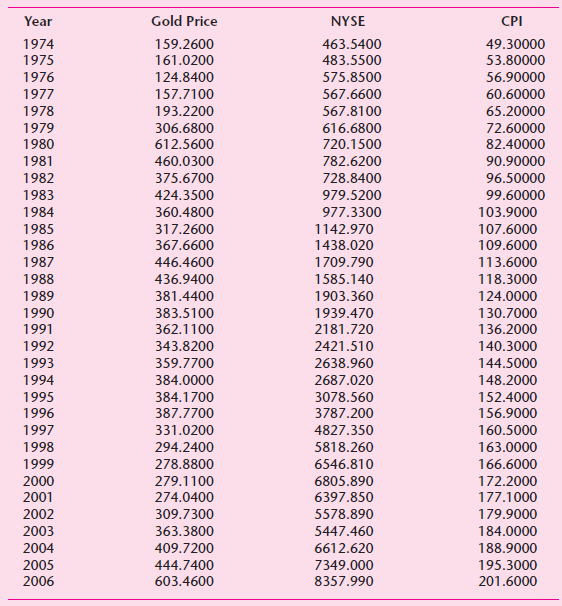
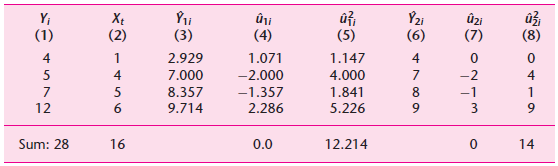
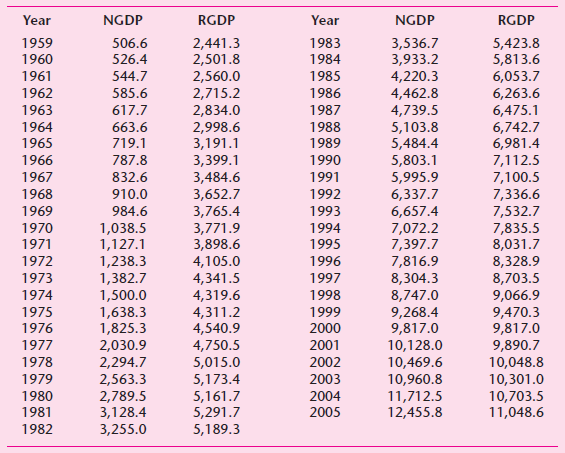
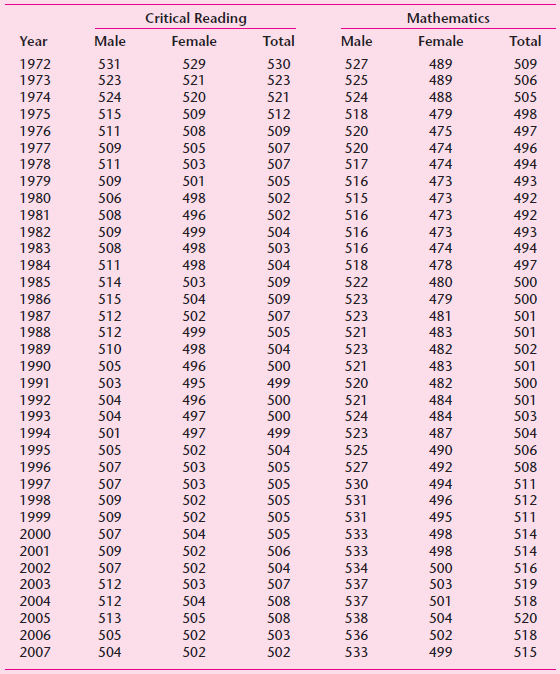
![Σxy / (Σx?) (ΣΥ?) η ΣΧΥ-(ΣΧ)(Σ Υ) [μΣΧ - (ΣΧ);]μ ΣΥ - (Σ] || ||](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1521/6/3/5/7075ab2517b129fcblob)