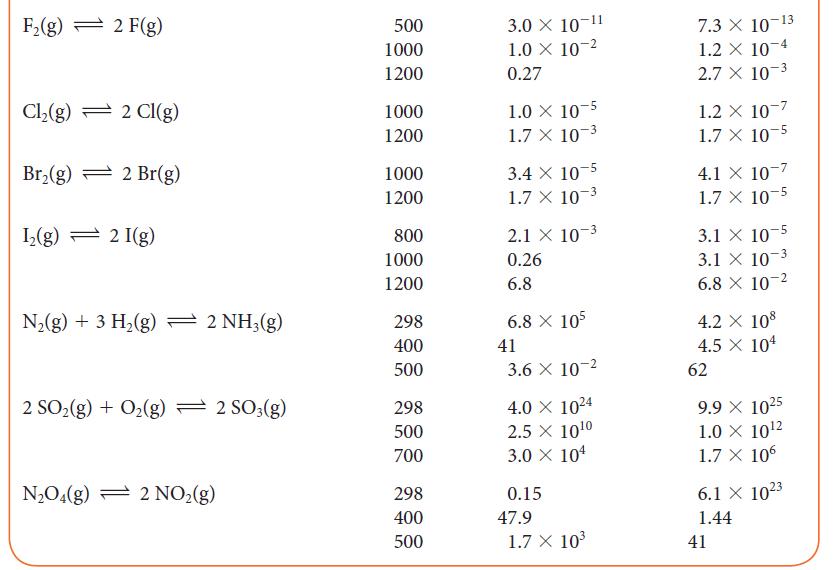
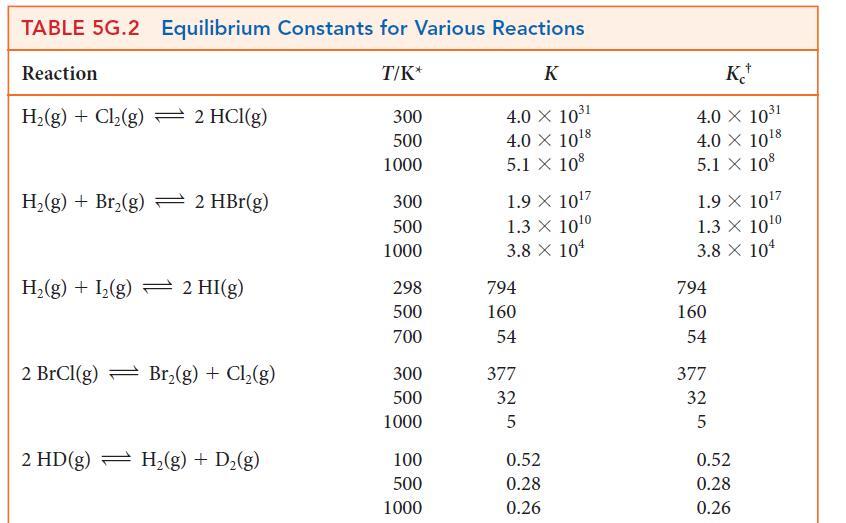
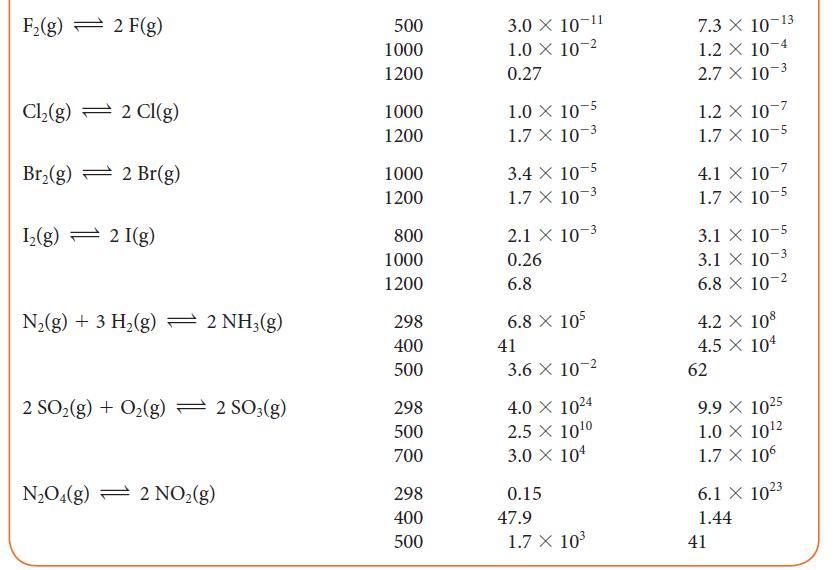
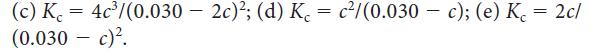![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


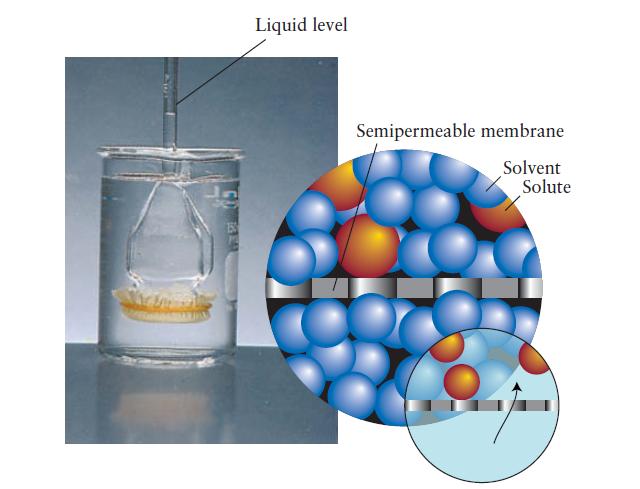
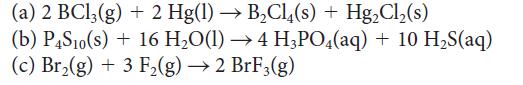
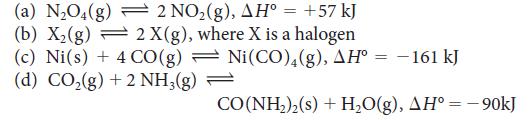
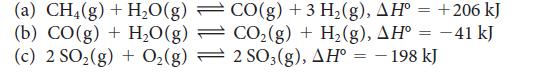
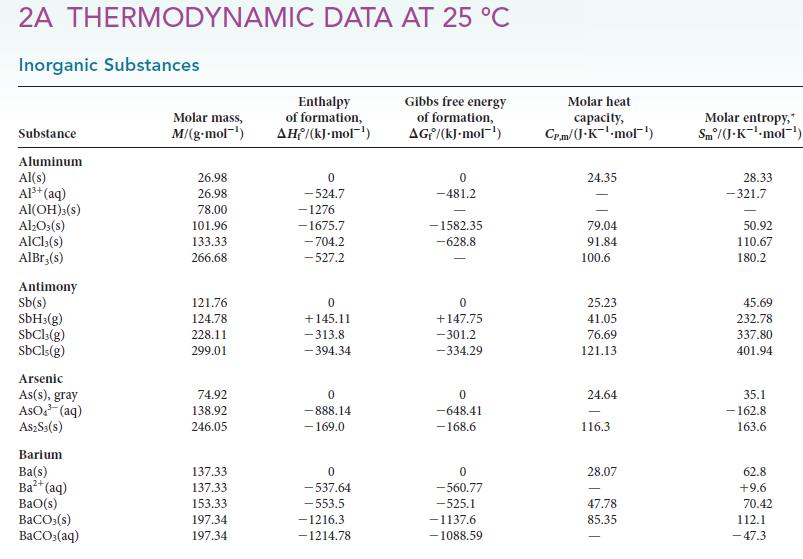
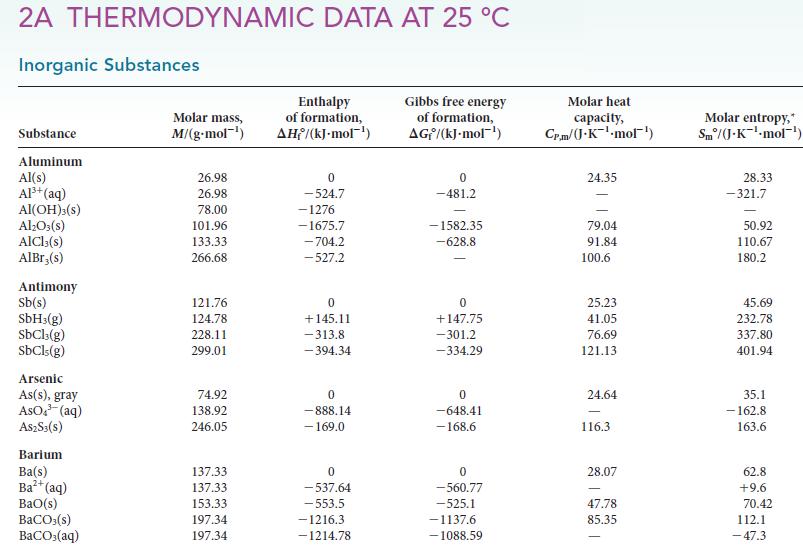
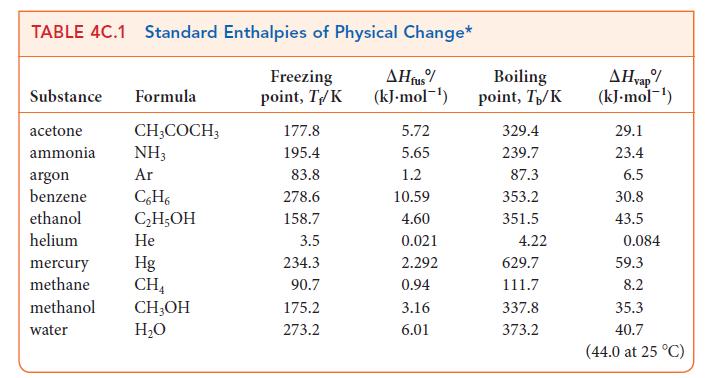
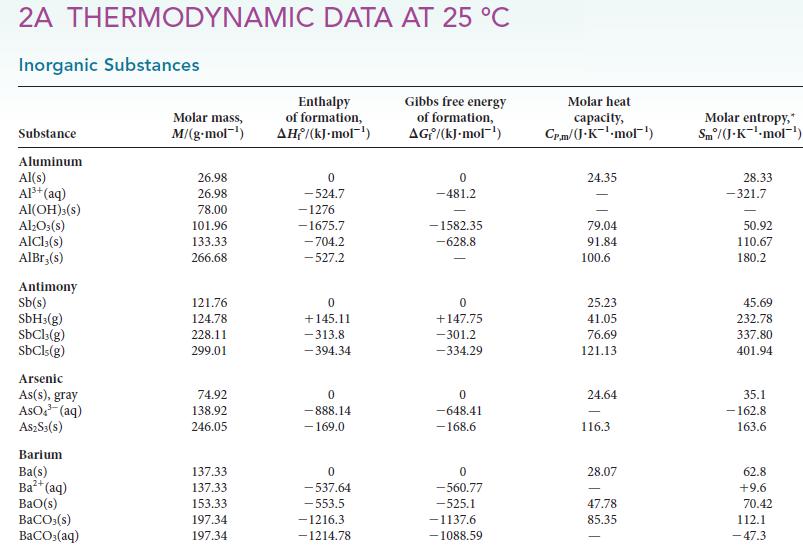
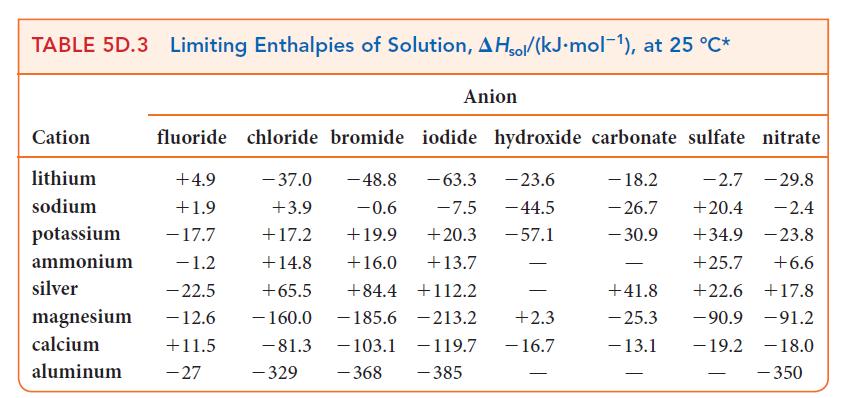
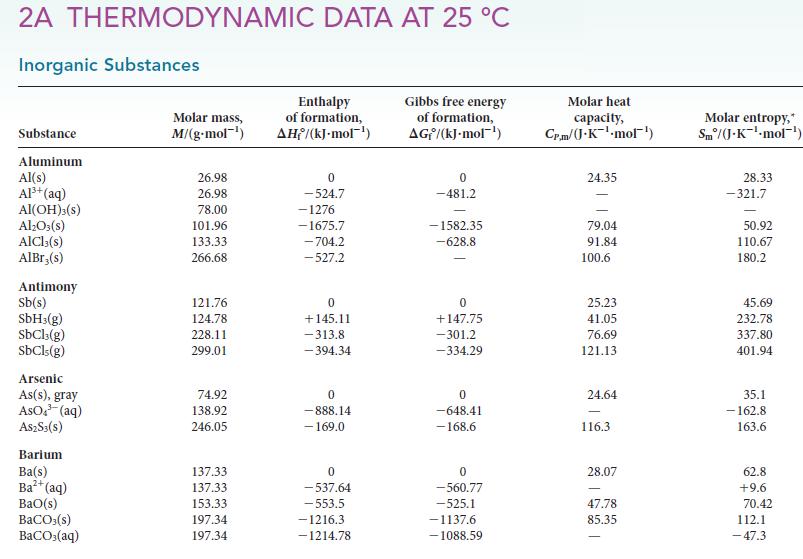
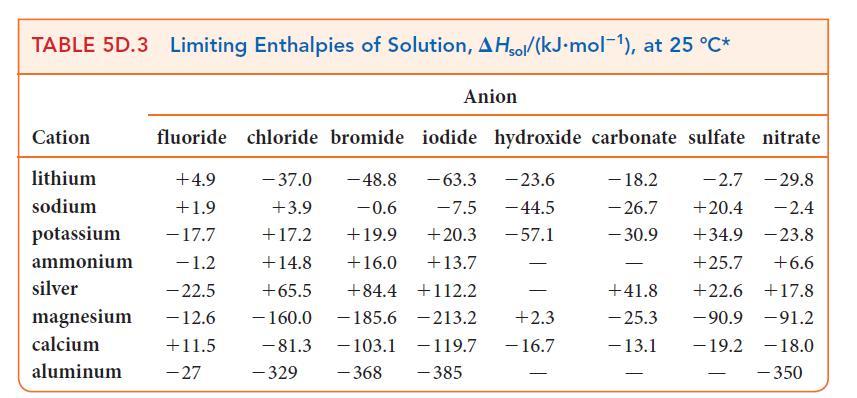
![Molar concentration, [J] (a) H, (reactant) NH, (product) N (reactant) Time, t Molar concentration, [J] (b) H](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1703/6/7/4/911658c041fb31a61703674910368.jpg)