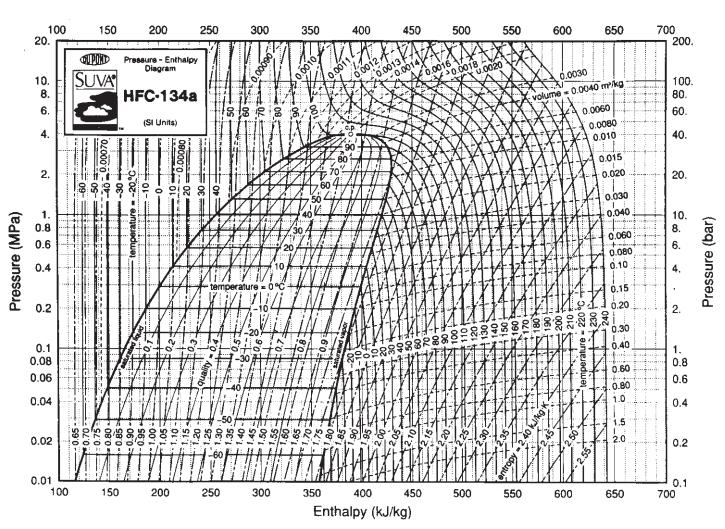
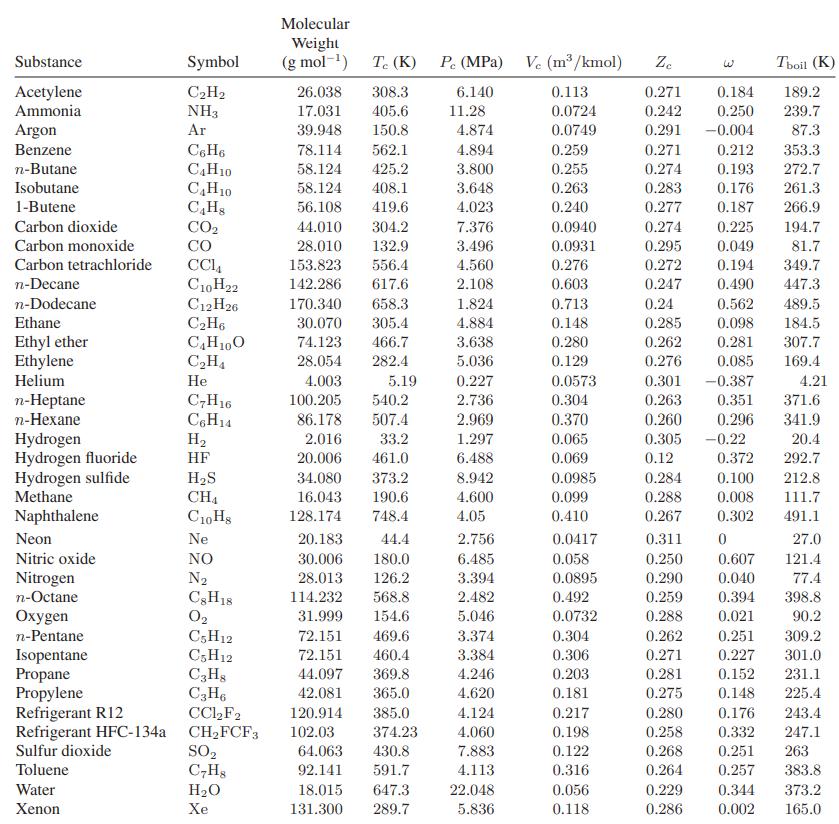
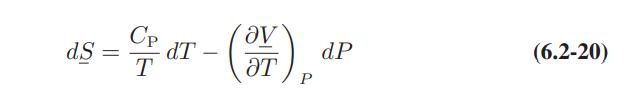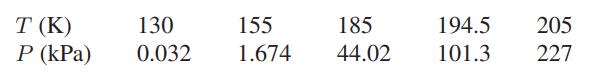![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


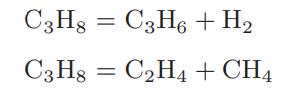
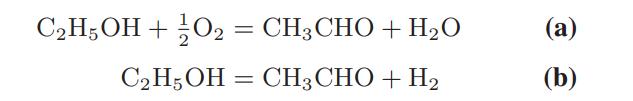
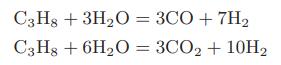
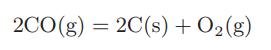
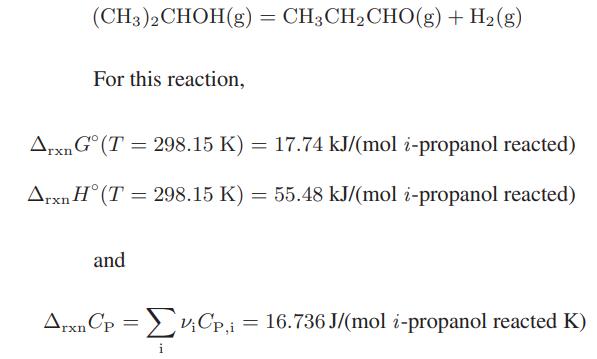
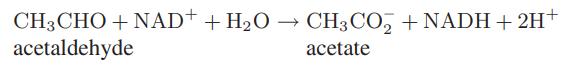
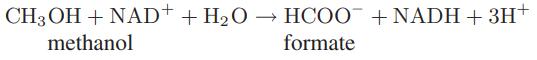
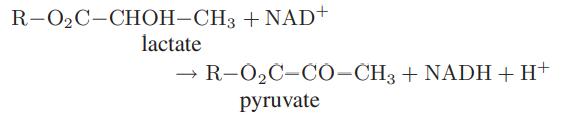
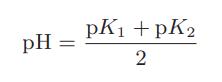
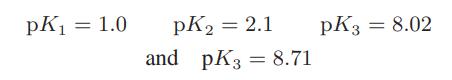
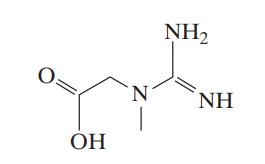
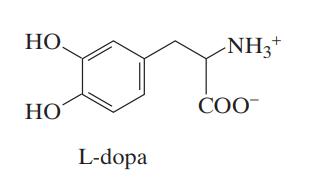
![Macid = MHA + MHA- + MA_ = MHA + K MHA 1+ [ = K MH+ + K (MH+)] . MHA. K MHA K K + MH+ (MH+) . (13.6-3)](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1700/2/2/1/940655753f45f5771700221935928.jpg)
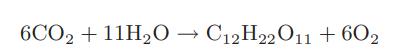
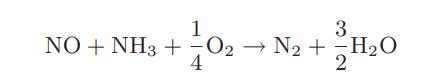
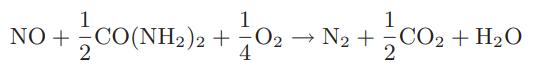
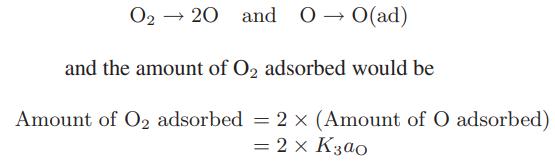
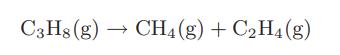
![CO (gas) CO (dissolved) with 1 KH = 29.76 atm - liter mol CO + HO HCO3 Kh HCO3 HCO3 + H+ = 1 [CO2] Pco2 KH](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1700/2/1/7/8966557442868c021700217893124.jpg)
![CO2(g) CO,(1) CO (1) + HO HCO3 HCO3 HCO3 + H+ [CO]H = Pco K = [HCO3] [CO2] [HCO][H+] [HCO3] K2 =](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1700/2/1/7/820655743dcc5ce31700217817668.jpg)
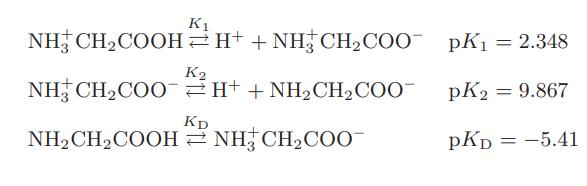
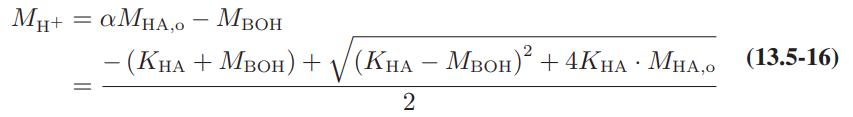
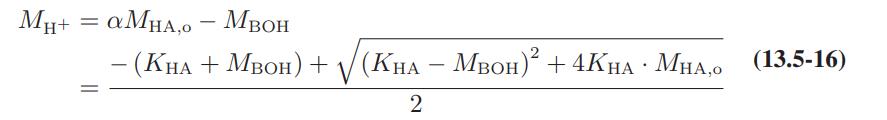
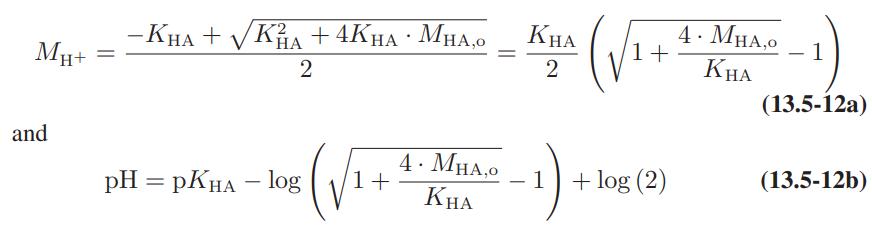
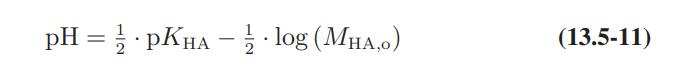
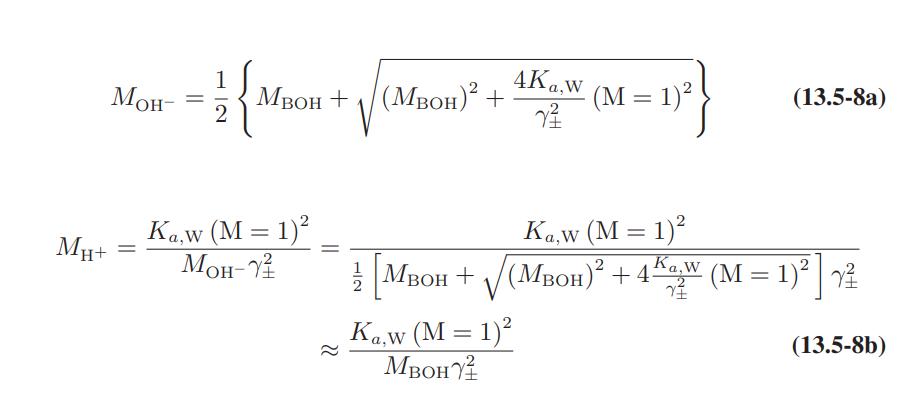
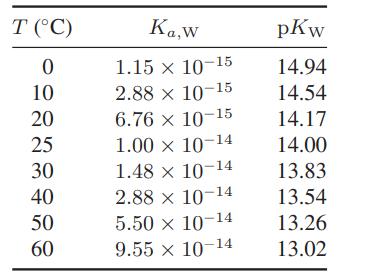
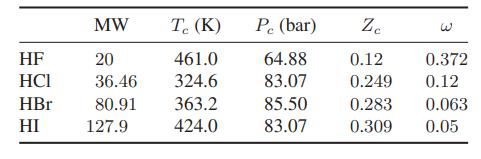
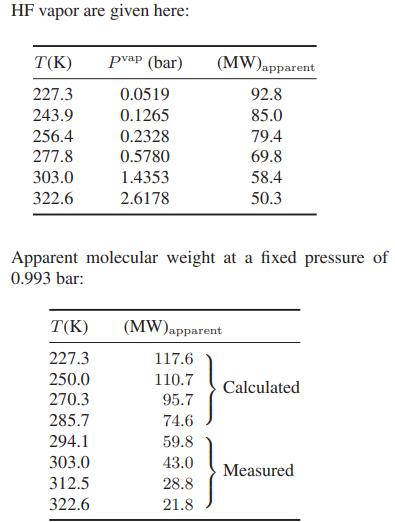
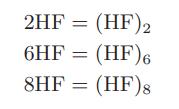
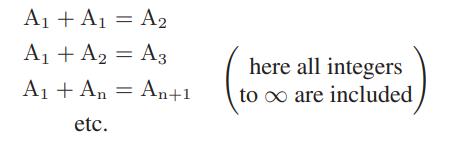
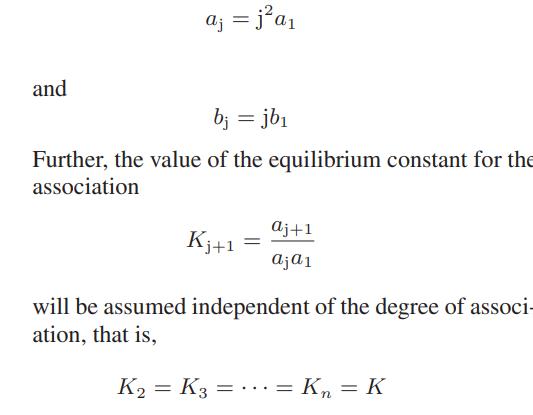
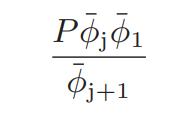
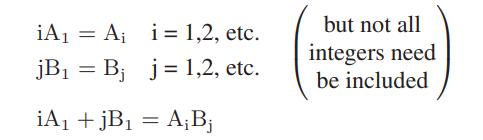
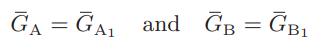

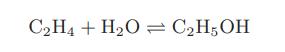
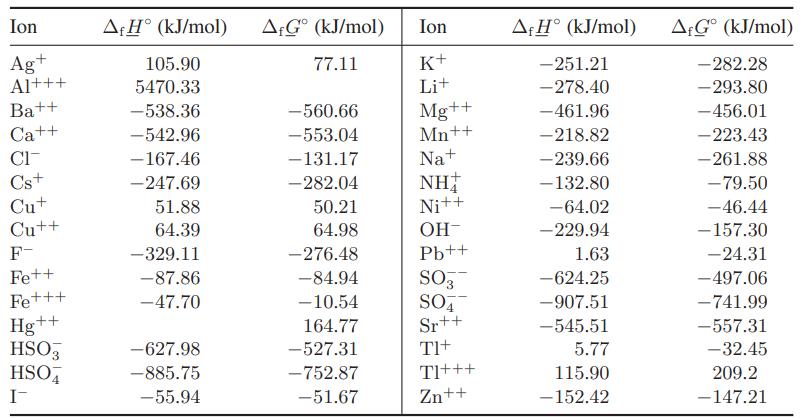
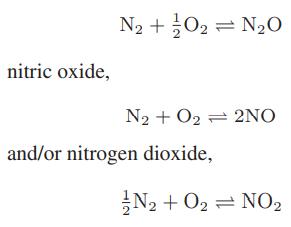
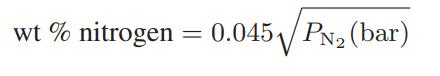
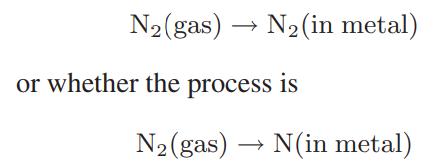
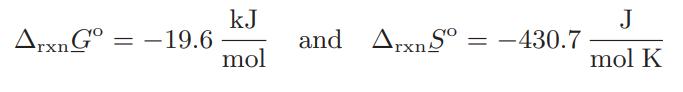
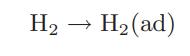

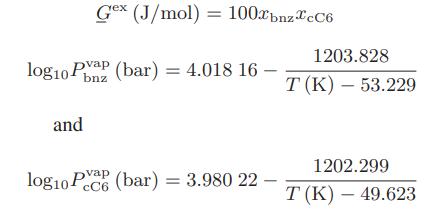
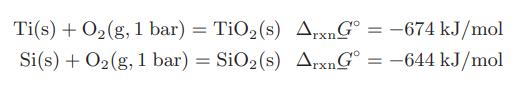
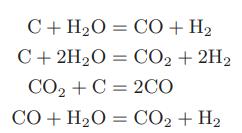
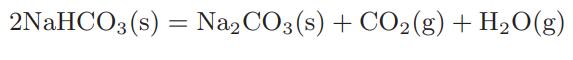
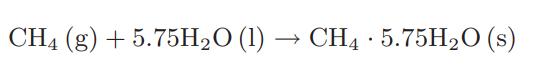
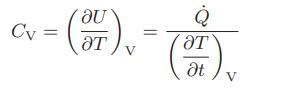
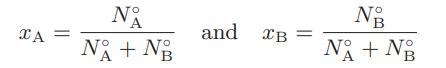
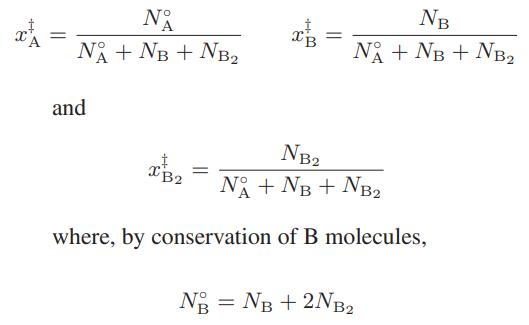
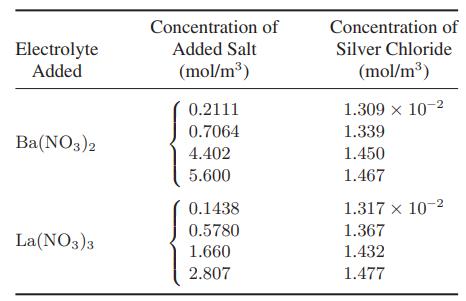
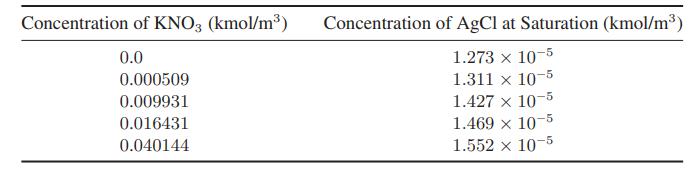
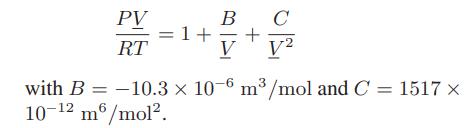
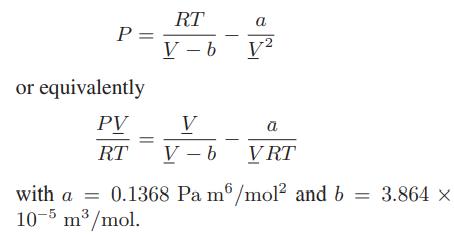
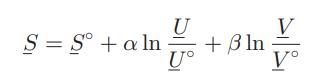
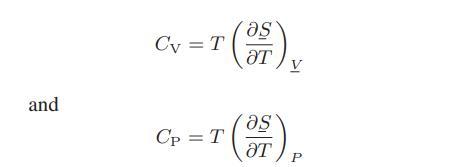
![as 'U C),-), ),-), [C).] = T V V V U V = Cv|T (6.2-18)](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1700/0/4/0/09265548d9c4aa281700040090435.jpg)